NAD
Definition
NAD (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide) is a coenzyme found in all living cells that plays a crucial role in various biological processes, including energy production, DNA repair, and gene expression regulation. It is involved in cellular metabolism and is essential for maintaining overall health and longevity. NAD levels decline with age, and supplementing with NAD precursors has been studied for its potential anti-aging effects.



Summary
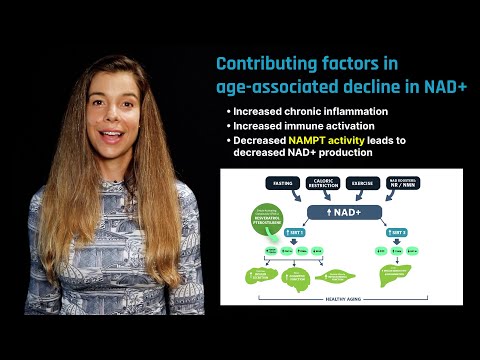
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) is a vital coenzyme present in all living cells, essential for energy production, DNA repair, and gene regulation. As we age, NAD levels decline, which can lead to age-related diseases and mitochondrial dysfunction. Research suggests that supplementing with NAD precursors like nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) and nicotinamide riboside (NR) may enhance cellular function and combat some aging effects, although human studies show mixed results. Additionally, NAD activates sirtuins, proteins crucial for cellular health and defense against oxidative stress and inflammation. Lifestyle factors such as regular exercise, a balanced diet, and fasting can also influence NAD levels and overall longevity. While NAD boosters show promise, a comprehensive approach that includes healthy lifestyle choices is vital for promoting health and longevity. Ongoing research into aging mechanisms, including gene therapies and epigenetic reprogramming, holds potential for innovative therapies to enhance quality of life as we age.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
Q: What is NAD and its role in the body?
NAD, or nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, is a crucial molecule in the body that plays a significant role in energy metabolism and various biological processes related to aging. 1. Energy Production: NAD is essential for the production of energy in cells. It is involved in the mitochondrial energy production cycle, where it helps convert nutrient…... Learn about NAD's importance -
Q: How does aging affect NAD levels?
Aging significantly impacts NAD (Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide) levels in the body, primarily through two mechanisms: increased utilization and decreased production.1. Decreased NAD Levels with Age: As individuals age, NAD levels decline, which is associated with a decrease in the efficiency of various enzymes, including sirtuins that rely on …... Explore aging and NAD -
Q: What are NAD precursors and their benefits?
NAD precursors are compounds that the body can convert into nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+), a crucial molecule involved in various cellular processes, including energy production, DNA repair, and regulation of cellular metabolism. The most commonly discussed NAD precursors are nicotinamide riboside (NR) and nicotinamide mononucleotide (N…... Discover NAD precursors -
Q: How do lifestyle factors influence aging?
Lifestyle factors significantly influence aging through various mechanisms, impacting both biological and chronological aging. Here are some key insights gathered from the videos:1. Diet and Nutrition: A plant-based diet is associated with decreased epigenetic age, while poor dietary choices, such as obesity, can accelerate aging and increase the …... Understand lifestyle impacts -
Q: What is the future of aging research?
The future of aging research is poised for significant advancements, focusing on understanding the underlying mechanisms of aging and developing interventions to enhance healthspan and lifespan. Here are some key insights from various experts in the field:1. Biomarkers of Aging: Dr. Eric Verdin emphasizes the need for reliable biomarkers to assess…... Explore future research directions
Related Topics
Aging | Longevity | Sirtuins | NMN | Resveratrol
